Note: Service details can vary between engines and from the customer's requests. These are the common procedures for most rebuilds, and performance modifications.
In-Depth Explanation of Services
Rebuilds Explained
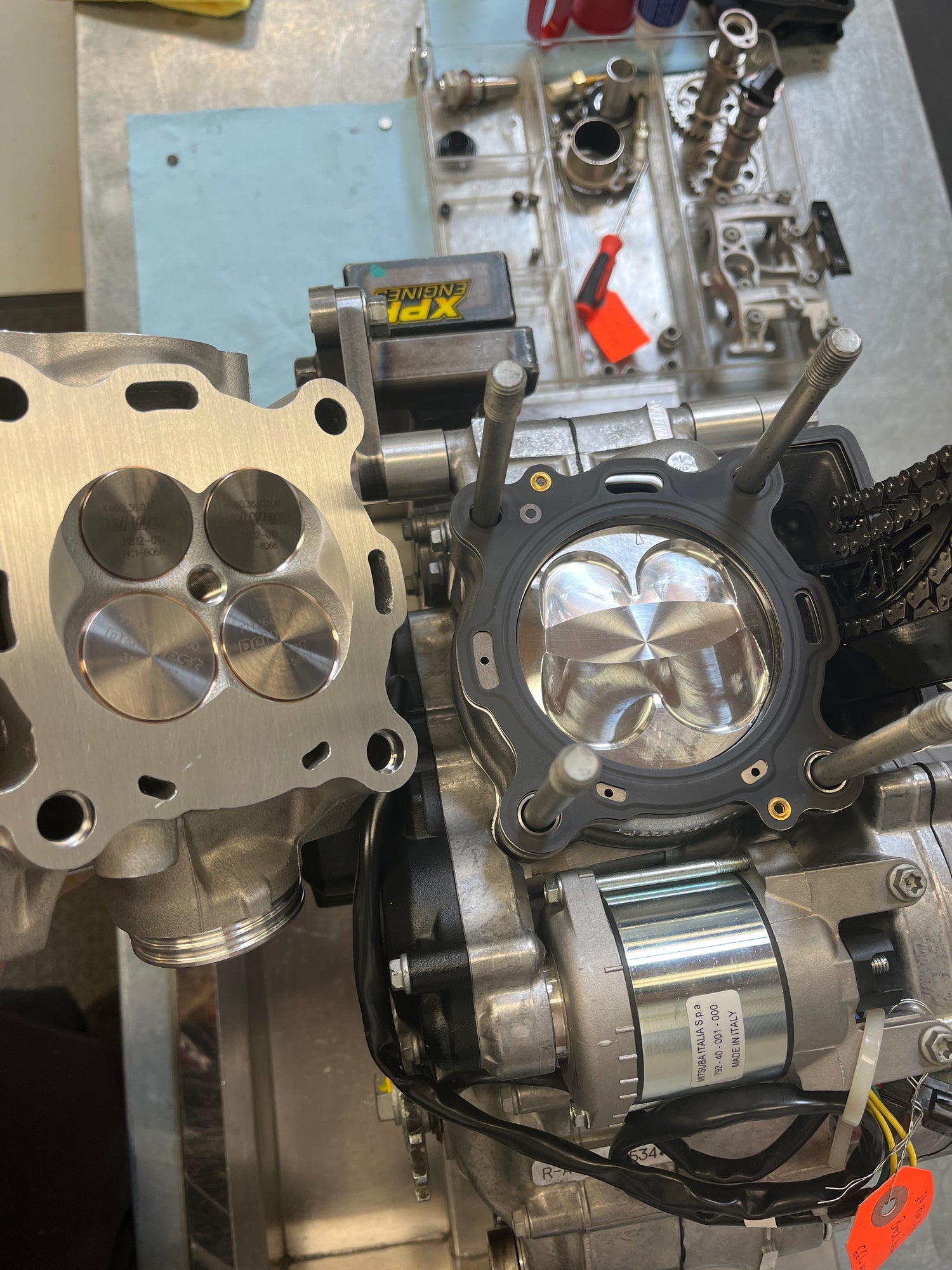
4 Stroke Top-End Rebuilds
Consist of: New valves and valve seats. Cleaning and inspection of ports, surfacing the head, surfacing and honing the cylinder, checking the connecting rod’s bushing tolerances, replacing the complete piston and rings, temperature sensor, spark plug and old gaskets.
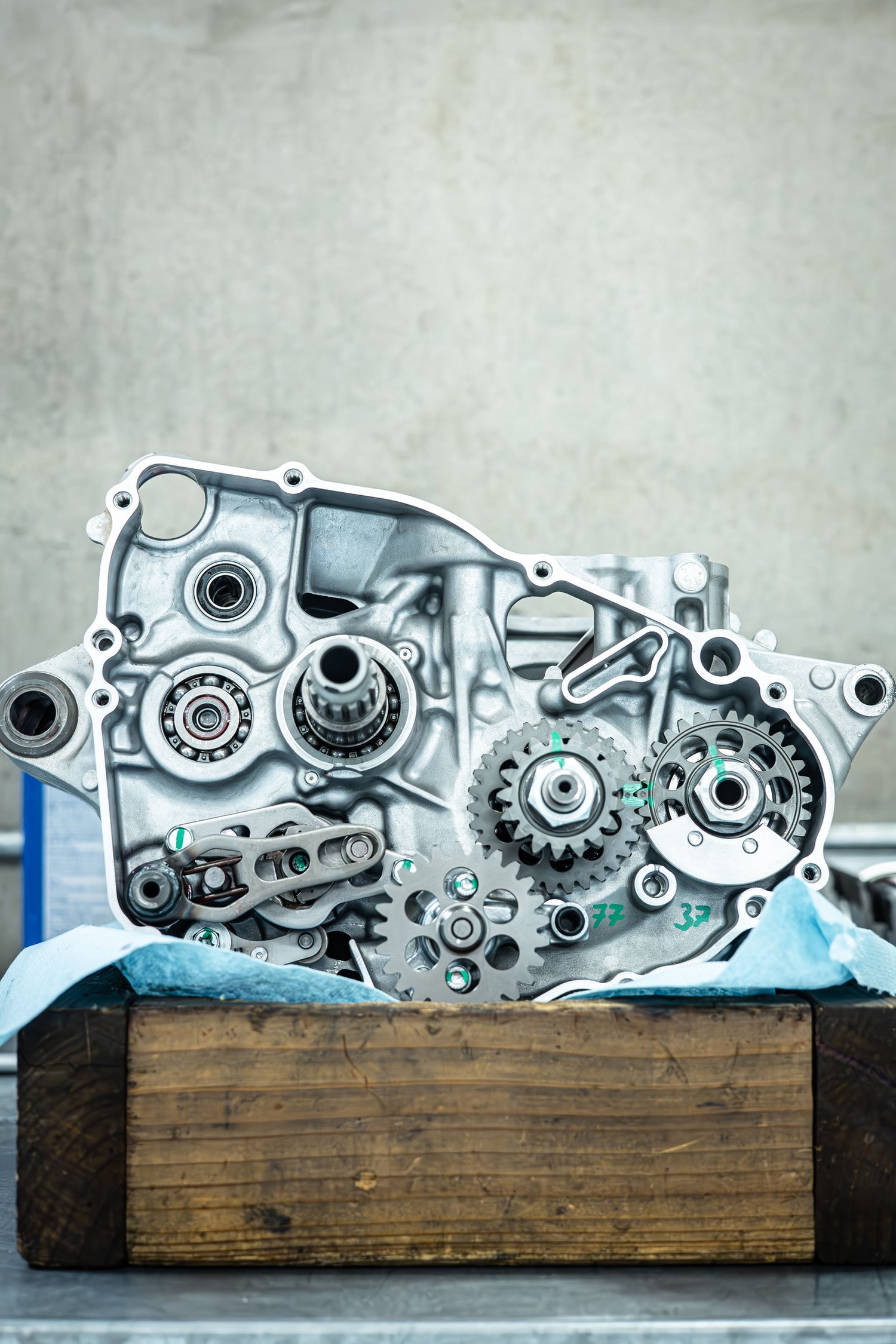
2 and 4 Stroke Bottom-End Rebuilds
Consist of: Disassembly of entire engine and splitting of the cases. Inspection/replacement of damaged transmission gears, and clutch components. Gaskets are replaced, as well as a crank rebuild, depending on hours of the bike and the condition of the small end of the connecting rod. Typically, the seals are replaced along with any other old/damaged parts.
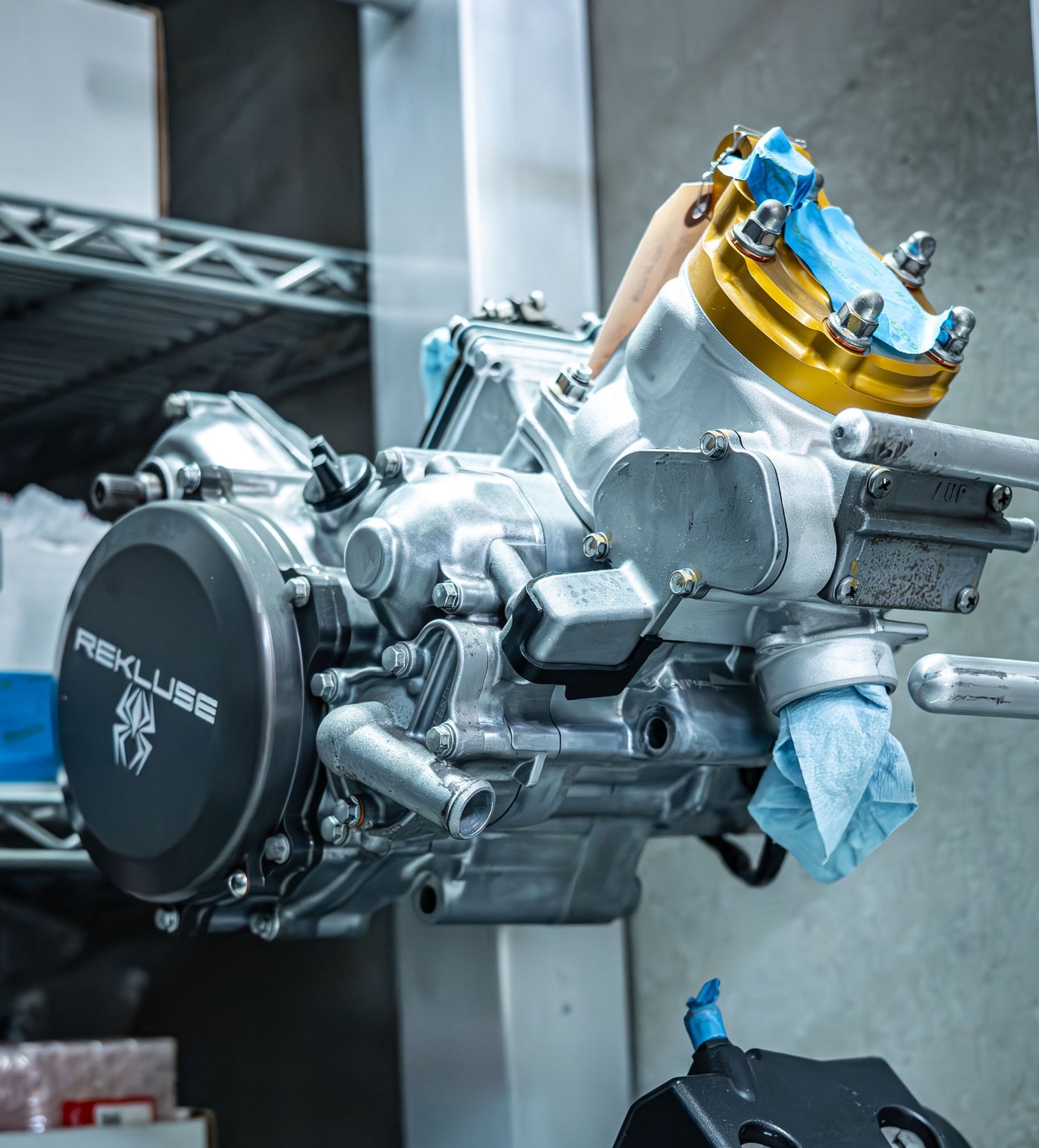
2 Stroke Top-End Rebuilds
Consist of: Cleaning/inspection of ports and power valve. Surfacing and honing the cylinder, checking the connecting rod’s bushing tolerances, "squish" clearance, and replacing the complete piston, piston rings, spark plug and old gaskets/o-rings.
Performance Modifications
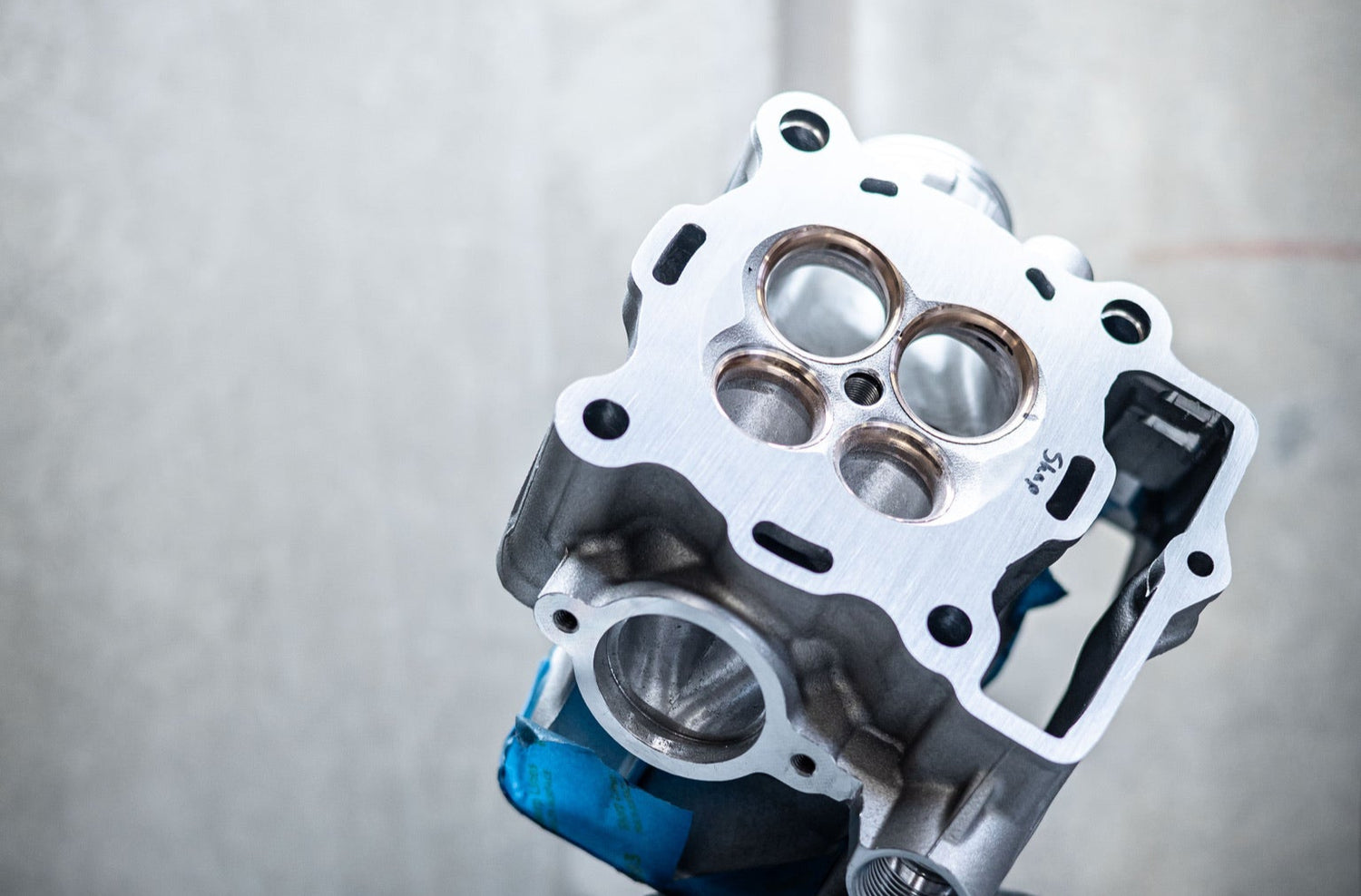
4 Stroke Top-End Mods
Consist of: Installing copper valve seats, performance porting, high compression pistons, custom-spec valves, high performance intake springs, XPR custom camshafts, and improvement of valve clearances.
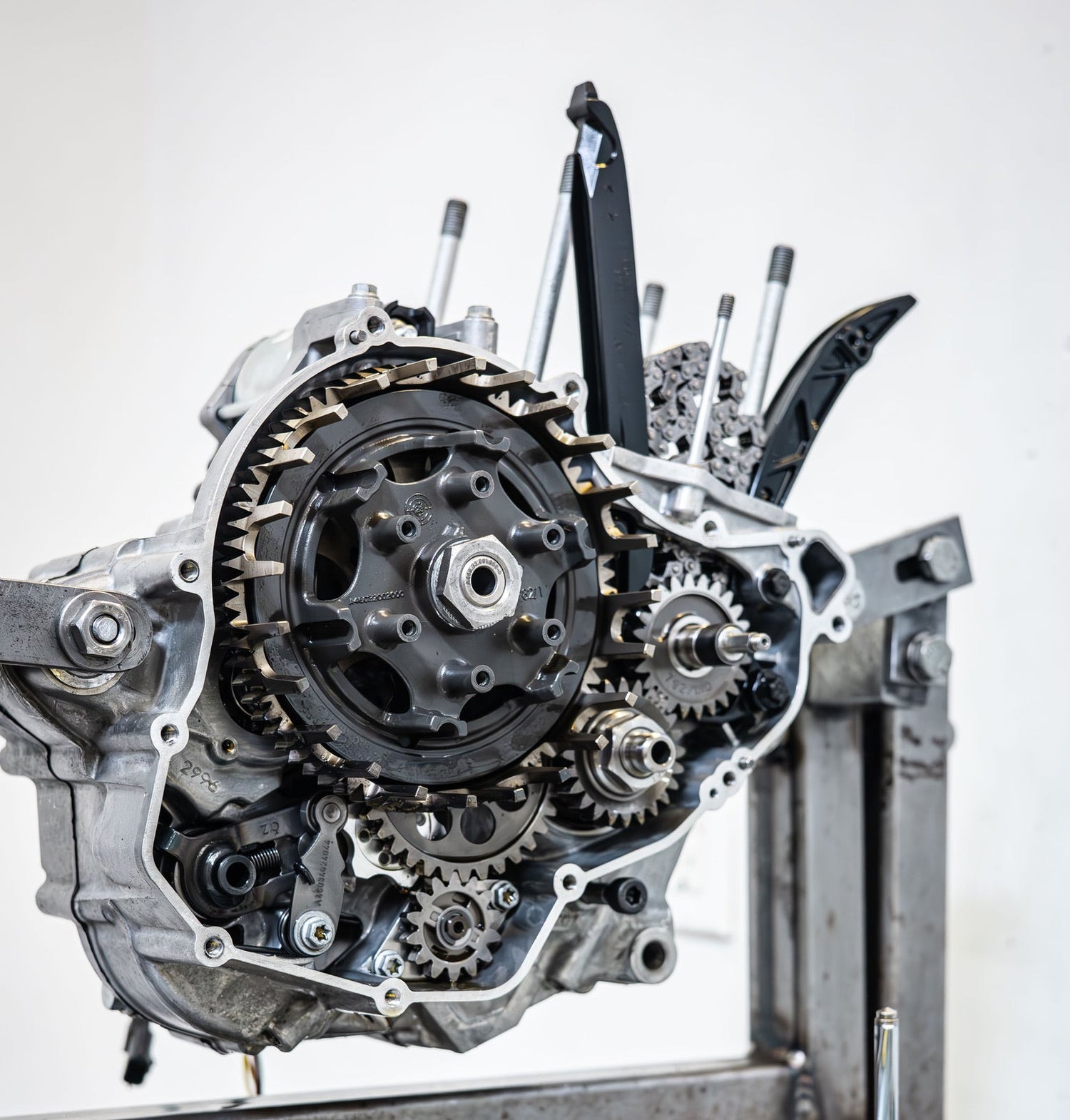
Bottom-End Mods
Consist of: Transmission treatment, crank modifications, and race-spec clutch components.
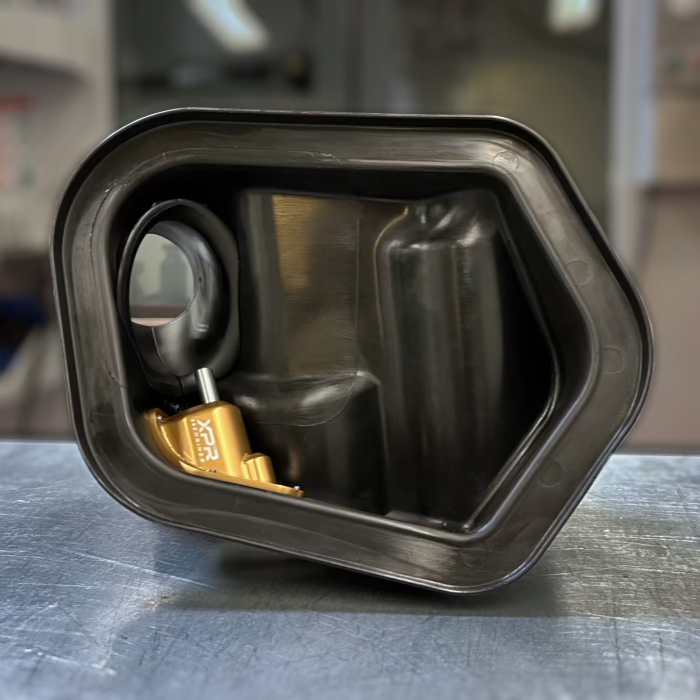

Combustion Efficiency Mods
Consist of: Vortex ECUs, dyno tuning, and custom 2nd injector setups.
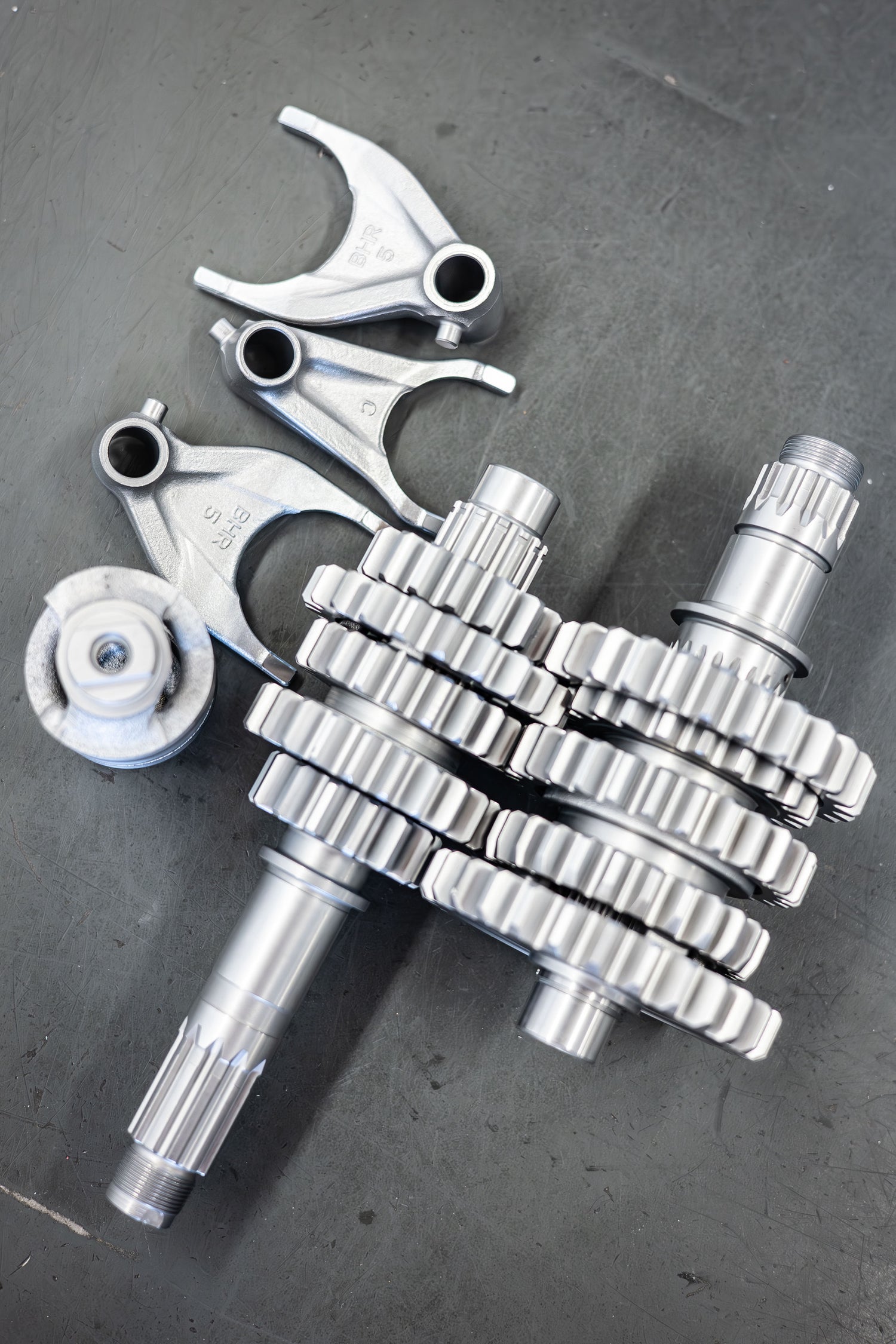

Transmission Treatments
Stock transmissions usually have rough surfaces, along with burrs on the edges, and sometimes defects. This effects how the gears contact and mesh with each other, causing unnecessary friction and wear. A transmission treatment at XPR is a 5-stage process:
- Disassemble and inspection (We assure that the gears have no defects)
- De-burring (Get rid of burrs for smoother gear engagement)
- Peening (Surface hardening)
- Media tumble (for reduced friction)
- Reassembly
This process provides smoother, faster, easier shifts under power, a longer lasting transmission with less wear, increased shift confidence leading to faster times, and lowers operating temperatures.
